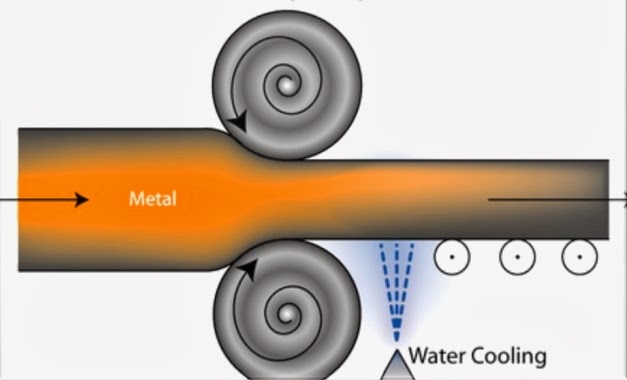
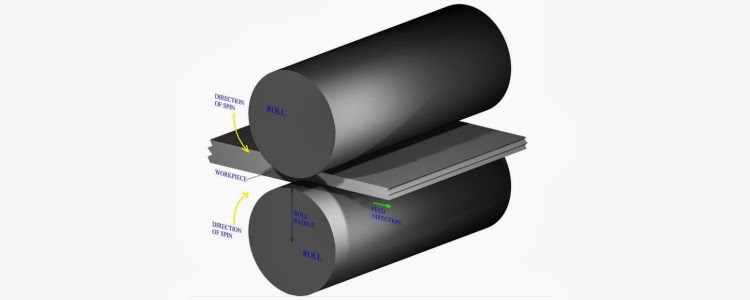
Work Hardening also referred commonly as cold working or strain hardening process leads to strengthening of metal by its plastic deformation. The strengthening of metal is caused by the dislocation movements and dislocation generation occurring within the crystal structure of material. In metal-working processes, work-hardening stimulates plastic deformation to exact a shape change in metals. This is characterized by shaping the workpiece at temperature below its recrystallization temperature; usually at ambient temperature. At any time, the effects induced by work-hardening can be reversed by process called annealing carried at high temperatures, where recovery and recrystallization reduces the dislocation density.
Cold working can be applied to numerous non-brittle metals having high melting points as well as to several polymers to strengthen them. Other ,metal-alloys which cannot be amended by heat-treatment such as low carbon steel is also frequently hardened. Metals like copper and aluminum are most frequently work-hardened at normal temperatures.
Cold forming techniques are mostly classified into for major categories:
- Drawing
- Squeezing
- Shearing
- Bending
These applications generally produce final products like blots and screws and also finished cold rolled steel. Cold forming processes involve metal-working at high speed and high pressure using carbide dies or toll steel. Cold working is advantageous to metal-working as it increases the yield strength, hardness and tensile strength of work-piece. The further sections speak on the advantages as well as disadvantages of cold-forming process.
Read further on http://www.wiredrawingdies.co.in/cold-forming/. You can check our other products and services on www.wiredrawingdies.co.in